Search results
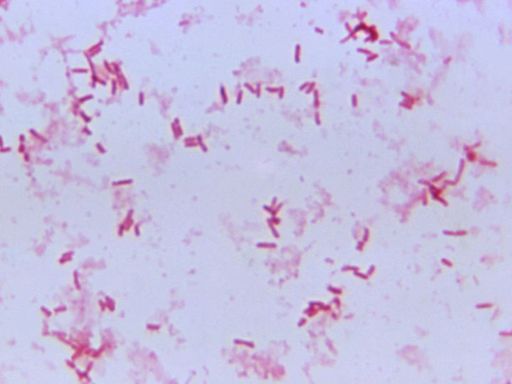
4 days ago · The disease is caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis and spread by fleas and through the air. [4] [5] One of the most significant events in European history, the Black Death had far-reaching population, economic, and cultural impacts. It was the beginning of the second plague pandemic. [6]
Jun 21, 2024 · Black Death, pandemic that ravaged Europe between 1347 and 1351, taking a proportionately greater toll of life than any other known epidemic or war up to that time. The Black Death is widely thought to have been the result of plague, caused by infection with the bacterium Yersinia pestis.
Jun 21, 2024 · Black Death - Bubonic Plague, Europe, 1347: The plague originated in Asia, and entered Europe in 1347 when Janibeg catapulted plague-infested corpses into the besieged port of Kaffa (now Feodosiya) in Crimea. From Kaffa, Genoese ships carried the epidemic westward to the rest of Europe, and the plague reached northern Europe by 1350.
Jun 21, 2024 · Black Death - Plague, Mortality, Europe: It is estimated that 25 million people, or about a third of the population, died in Europe from plague during the pandemic. This massive loss of life led to many changes, including much less land under cultivation, greater social mobility, and a rise in violent anti-Semitism because Jews were ...
21 hours ago · Plague, one of the deadliest bacterial infections in human history, caused an estimated 50 million deaths in Europe during the Middle Ages when it was known as the Black Death.
Jun 17, 2024 · Plague is an acute, contagious, febrile illness usually transmitted to humans by the bite of an infected flea. Plague occurs as 3 major clinical events: bubonic plague, septicemic plague, and...
Jun 21, 2024 · Plague, caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, is a disease that affects humans and other mammals. People typically get infected after being bitten by a rodent flea that is carrying the bacterium or by handling a plague-infected animal.